Clean Room Classifications: Understanding the Different Types and Their Uses
- 2024-02-05
- View 13
Cleanrooms are specialized environments that are designed to maintain a controlled level of cleanliness. These rooms are used in a variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics, and aerospace. In this article, we will explore the different clean room classifications the standards used to define them, and their respective applications.
Understanding Clean Room Classifications
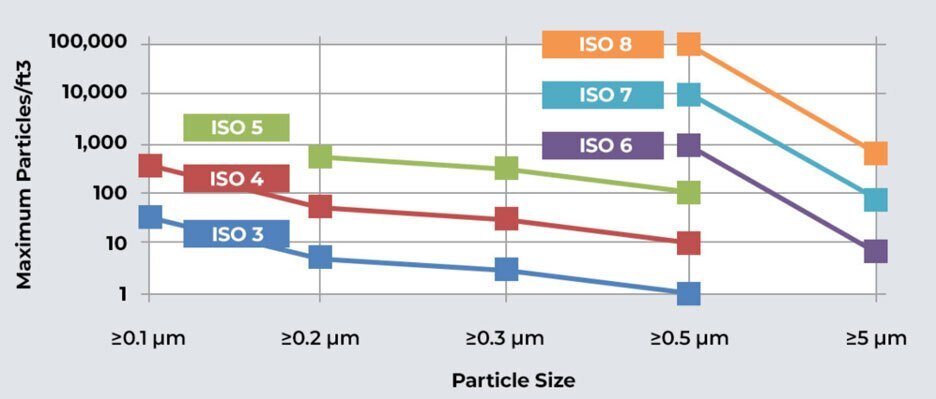
Cleanrooms are classified based on the level of cleanliness they maintain. The classification system is based on the number and size of particles allowed per cubic meter of air in the cleanroom The ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and the US Federal Standard 209E are two commonly used standards for clean room classification.
ISO Clean Room Classification
The ISO classification system ranges from ISO Class 1 (the cleanest) to ISO Class 9 (the least clean). Each ISO class corresponds to a specific number of particles per cubic meter of air. Here is a breakdown of the ISO cleanroom classification:
ISO Class 1: <10 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 2: <100 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 3: <1,000 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 4: <10,000 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 5: <100,000 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 6: <1,000,000 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 7: <10,000,000 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 8: <100,000,000 particles per cubic meter of air
ISO Class 9: >100,000,000 particles per cubic meter of air
Federal Standard 209E Clean Room Classification
The Federal Standard 209E classification system was developed by the US Federal Government in 1963 and ranges from Class 1 (the cleanest) to Class 100,000 (the least clean). Here is a breakdown of the Federal Standard 209E cleanroom classification:
Class 1: <1 particle per cubic foot of air
Class 10: <10 particles per cubic foot of air
Class 100: <100 particles per cubic foot of air
Class 1,000: <1,000 particles per cubic foot of air
Class 10,000: <10,000 particles per cubic foot of air
Class 100,000: <100,000 particles per cubic foot of air
Cleanroom Applications
Different industries have different requirements for cleanroom classification based on their specific applications. Here are some examples of industries that use cleanrooms and their respective clean room classifications:
Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries use cleanrooms to manufacture drugs and medical devices. These cleanrooms must meet ISO Class 5 or higher standards to prevent contamination of the products being manufactured.
Electronics
The electronics industry uses cleanrooms to manufacture microchips, semiconductors, and other electronic components. These cleanrooms must meet ISO Class 1 or higher standards to prevent contamination that could impact the performance of the products being manufactured.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry uses cleanrooms to manufacture spacecraft, satellites, and other aerospace components. These cleanrooms must meet ISO Class 8 or higher standards to prevent contamination that could impact the performance and safety of the products being manufactured.
Hospitals and Healthcare
Hospitals and healthcare facilities use cleanrooms for sterile environments in operating rooms, isolation rooms, and laboratories. These cleanrooms must meet ISO Class 5 or higher standards to prevent the spread of infection and to protect patients and healthcare workers.
Maintaining Cleanroom Standards
Maintaining cleanroom standards requires strict adherence to a set of protocols that are designed to prevent contamination. Some of these protocols include:
Air Filtration
Cleanrooms use high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to remove particles from the air. These filters can remove particles as small as 0.3 microns in size. Air is typically recirculated through the HEPA filters multiple times per hour to maintain the desired cleanliness level.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Cleanroom workers must wear PPE, including gowns, gloves, and masks, to prevent contamination from human sources. PPE must be properly cleaned and sanitized before entering the cleanroom and discarded after leaving.
Cleanroom Design
Cleanroom design is critical to maintaining cleanliness levels. Cleanrooms must be designed to prevent the entry of contaminants and to facilitate the removal of particles. The design must also ensure that air flow is directed away from the cleanroom workers and products being manufactured.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Cleanrooms must be cleaned regularly to maintain the desired level of cleanliness. Surfaces must be wiped down with specific cleaning agents and techniques to prevent contamination. The cleanroom must also undergo regular maintenance to ensure that equipment is functioning properly and that the cleanroom remains in compliance with standards.
FAQs
What is the difference between ISO and Federal Standard 209E clean room classifications?
The ISO classification system ranges from ISO Class 1 (the cleanest) to ISO Class 9 (the least clean), while the Federal Standard 209E classification system ranges from Class 1 (the cleanest) to Class 100,000 (the least clean).
Why do pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries require ISO Class 5 or higher cleanrooms?
These industries require cleanrooms of this level to prevent contamination of the products being manufactured.
How do cleanrooms prevent contamination from human sources?
Cleanroom workers must wear personal protective equipment, including gowns, gloves, and masks, to prevent contamination from human sources.
How often should cleanrooms be cleaned?
Cleanrooms must be cleaned regularly to maintain the desired level of cleanliness.
What is the purpose of air filtration in cleanrooms?
Air filtration in cleanrooms is critical to removing particles from the air to maintain the desired level of cleanliness.
Conclusion
Clean room classifications play a critical role in maintaining the desired level of cleanliness for various industries. Understanding the different classifications and their corresponding applications is essential to ensure that products are manufactured to the required standards. Maintaining cleanroom standards requires strict adherence to protocols that include air filtration, personal protective equipment cleanroom design and cleaning and maintenance.
