Cleanroom Design and Build: Creating Controlled Environments for Precision Industries
- 2024-01-24
- View 10
Cleanrooms are critical in industries that require strict control over contamination levels to maintain product quality and ensure the safety of personnel Cleanroom design and build involve meticulous planning and execution to create controlled environments that adhere to specific cleanliness standards. In this article, we will delve into the key aspects of cleanroom design and construction, highlighting the importance of cleanroom classification layout, HVAC systems, and other essential considerations.
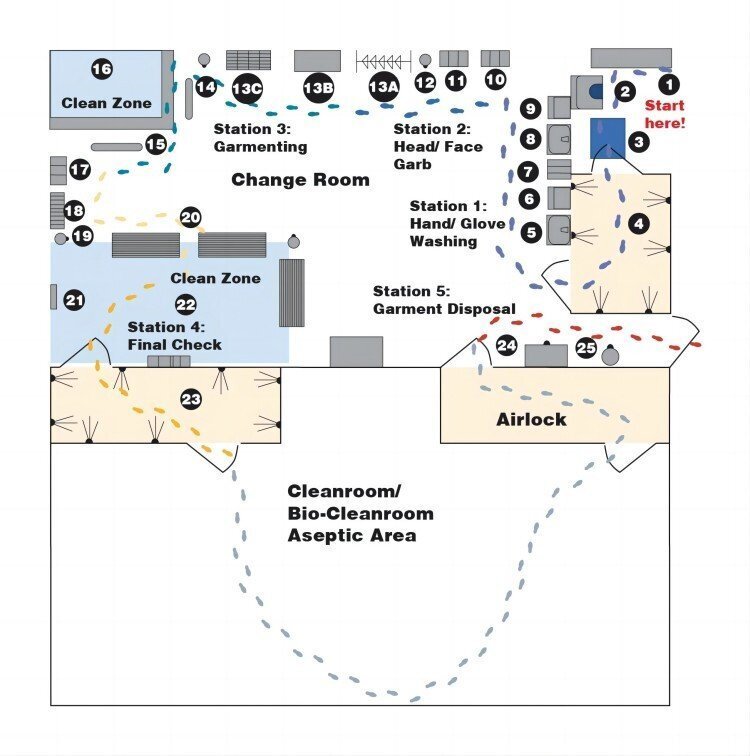
Understanding Cleanroom Requirements
The Role of Cleanroom Design
Cleanroom design plays a pivotal role in creating controlled environments where the level of airborne particles is kept to a minimum. Proper design ensures the cleanroom meets the specific needs of the industry it serves.
Cleanroom Classification and Standards
Cleanrooms are classified based on the allowable particle count in the air. The classification ranges from ISO Class 1 (highest cleanliness) to ISO Class 9 (lowest cleanliness). Industries determine the appropriate cleanroom class based on their specific requirements.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Cleanroom design must comply with relevant industry regulations, such as Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and International Organization for Standardization (ISO) guidelines, to ensure product quality and safety.
Cleanroom Design Process
The cleanroom design process involves several crucial steps that ensure the successful creation of a controlled environment.
Identifying Project Objectives
Understanding the project's objectives and requirements is the first step in designing a cleanroom. Factors such as the type of industry, products manufactured, and desired cleanliness level are crucial in this phase.
Determining Cleanroom Class
Based on the industry and required cleanliness level, the cleanroom class is determined. This classification guides the subsequent design and construction processes.
Selecting the Cleanroom Location
Choosing the right location for the cleanroom is essential to minimize external contamination sources and ensure smooth operations.
Establishing Layout and Floor Plan
The cleanroom layout and floor plan are designed to optimize workflow, minimize traffic, and segregate different cleanroom areas based on cleanliness requirements.
Integrating HVAC Systems
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are critical in maintaining the required cleanliness and temperature levels in the cleanroom.
Implementing Contamination Control Measures
Contamination control measures, such as air showers pass-through chambers, and gowning areas, are integrated into the cleanroom design to minimize the introduction of contaminants.
Incorporating ESD Protection
If the cleanroom deals with electronic components, Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection measures are included to prevent damage to sensitive electronics.
Considering Future Scalability
Designing the cleanroom with future scalability in mind allows for easier expansion or modification as the industry's needs change.
Cleanroom Construction
Once the design phase is complete cleanroom construction can begin. This phase requires careful execution and attention to detail.
Choosing Suitable Construction Materials
Construction materials must meet stringent cleanliness standards and be compatible with cleanroom requirements.
Working with Specialized Contractors
Cleanroom construction often requires collaboration with specialized contractors experienced in cleanroom design and build.
Monitoring and Quality Assurance
Regular monitoring and quality assurance checks are performed throughout the construction process to ensure adherence to design specifications.
Ensuring Adherence to Design Specifications
The construction team must strictly adhere to the approved cleanroom design and avoid deviations that could compromise the cleanroom's integrity.
Certifications and Testing
Upon completion, the cleanroom undergoes testing and certification to verify that it meets the designated cleanliness level and industry standards.
Essential Equipment and Cleanroom Accessories
Apart from the physical structure cleanrooms require specific equipment and accessories to function effectively.
Cleanroom Furniture and Fixtures
Specialized cleanroom furniture and fixtures are designed to minimize particle generation and facilitate efficient operations.
HVAC Systems and Filtration
HVAC systems with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are crucial for maintaining clean air quality in the cleanroom.
Cleanroom Lighting
Cleanroom lighting must meet specific requirements to avoid shadows and minimize particle generation.
Cleanroom Garments and Personal Protective Equipment
Cleanroom personnel wear specialized garments and personal protective equipment (PPE) to prevent contamination.
Monitoring and Control Instruments
Cleanrooms are equipped with monitoring and control instruments to continuously assess environmental conditions and ensure compliance with cleanliness standards.
Cleanroom Validation and Qualification
Validation and qualification are essential steps in confirming the cleanroom's performance and adherence to design specifications.
The Purpose of Validation and Qualification
Validation and qualification procedures provide objective evidence that the cleanroom consistently meets cleanliness standards and operational requirements.
Installation Qualification (IQ)
IQ ensures that all components and equipment are installed correctly according to the approved design and specifications.
Operational Qualification (OQ)
OQ verifies that the cleanroom operates as intended and achieves the required environmental conditions.
Performance Qualification (PQ)
PQ involves performance testing under dynamic conditions to demonstrate that the cleanroom can consistently maintain the specified cleanliness level.
Maintenance and Ongoing Monitoring
Once the cleanroom is operational, consistent maintenance and monitoring are crucial to sustain its functionality.
Establishing Maintenance Protocols
Routine maintenance protocols are established to ensure that all cleanroom equipment and systems are functioning properly and that potential issues are addressed promptly.
Routine Cleanroom Monitoring
Regular monitoring of the cleanroom environment is essential to identify any deviations from the required cleanliness levels. This includes monitoring airborne particle counts, temperature, humidity, and pressure differentials.
Addressing Contamination Incidents
In the event of a contamination incident, it is crucial to have well-defined protocols in place to identify the source of contamination, isolate affected areas, and take corrective actions to prevent reoccurrence.
Advancements in Cleanroom Design and Technology
The field of cleanroom design and technology is continually evolving, driven by the need for higher efficiency and improved contamination control. Some of the latest advancements include:
Modular Cleanroom Solutions
Modular cleanrooms offer flexibility and scalability, allowing for easier modifications and expansions to meet changing requirements.
Cleanroom Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are being integrated into cleanrooms to enhance precision and reduce human intervention, thereby minimizing the risk of human-induced contamination.
Energy-Efficient Cleanroom Systems
Advancements in energy-efficient HVAC systems and lighting solutions contribute to reducing operating costs and environmental impact.
Integration of IoT and Data Analytics
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analytics allows real-time monitoring of cleanroom conditions, predictive maintenance, and improved overall efficiency.
Conclusion
Cleanroom design and build are critical processes in creating controlled environments for industries that demand precise contamination control. Proper cleanroom design ensures that products are manufactured to the highest quality standards while safeguarding the health and safety of personnel. From selecting the appropriate cleanroom class to integrating advanced technology and ensuring ongoing maintenance, every aspect of cleanroom design contributes to the overall success and efficiency of the controlled environment.
By investing in thorough cleanroom design and construction, industries can gain a competitive edge by consistently delivering top-quality products and maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: How long does it take to design and build a cleanroom?
A: The time required for cleanroom design and construction can vary depending on the size, complexity, and industry requirements. It typically ranges from a few months to a year.
Q: Can cleanrooms be modified or expanded after construction?
A: Yes modular cleanroom solutions offer flexibility, making modifications and expansions relatively easier compared to traditional construction.
Q: Are there different types of cleanrooms based on industries?
A: Yes, cleanroom requirements vary based on the industry, and cleanrooms can be customized to meet the specific needs of pharmaceuticals, electronics, biotechnology, aerospace, and other industries.
Q: How often should cleanrooms be revalidated?
A: Cleanrooms should be revalidated periodically, usually every one to three years, or whenever there are significant changes to the cleanroom's design or processes.
Q: Can cleanroom automation replace human personnel entirely?
A: While cleanroom automation can enhance efficiency and reduce human-induced contamination risks, human personnel are still essential for oversight, decision-making, and handling complex tasks.
