Clean Room Classifications: Understanding the Different Levels of Cleanliness
- 2024-05-10
- View 11
Clean rooms are specialized environments designed to maintain controlled levels of particulate and microbial contamination. They are utilized in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics, healthcare, and aerospace, where cleanliness is crucial to ensure product quality, research integrity, and safety Clean rooms are classified based on the number and size of particles allowed per cubic meter of air. This article provides an overview of clean room classifications highlighting the different levels of cleanliness and their corresponding applications.
Class 1: The Strictest Clean Room Class
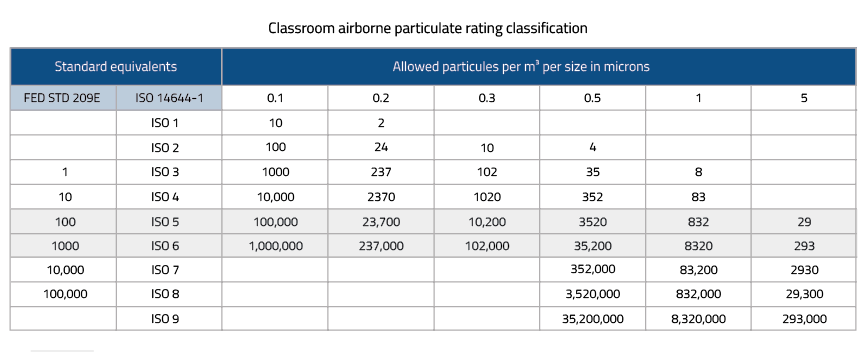
Class 1 clean rooms, also known as ISO Class 1 or Grade A clean rooms, have the strictest requirements for cleanliness. These clean rooms are designed to minimize particulate contamination and maintain an extremely clean environment. In a Class 1 clean room, the maximum allowable particle concentration is 1 particle of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. These clean rooms are typically used in critical industries such as microelectronics, nanotechnology, and advanced optics.
Class 10: Precision Manufacturing and Laboratory Research
Class 10 clean rooms, or ISO Class 3 clean rooms, have a slightly higher particle concentration limit compared to Class 1 clean rooms. The maximum allowable particle concentration in a Class 10 clean room is 10 particles of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. Class 10 clean rooms are commonly found in precision manufacturing facilities, research laboratories, and industries that require stringent cleanliness standards.
Class 100: High-Tech Manufacturing and Medical Devices
Class 100 clean rooms, or ISO Class 5 clean rooms, have a higher particle concentration limit compared to Class 10 clean rooms. The maximum allowable particle concentration in a Class 100 clean room is 100 particles of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. Class 100 clean rooms are utilized in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, medical device production, and pharmaceutical compounding.
Class 1,000: Assembly and Testing Environments
Class 1,000 clean rooms, or ISO Class 6 clean rooms, have a higher particle concentration limit compared to Class 100 clean rooms. The maximum allowable particle concentration in a Class 1,000 clean room is 1,000 particles of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. These clean rooms are commonly used for assembly, testing, and packaging processes in industries such as optics, automotive, and aerospace.
Class 10,000: Controlled Industrial Environments
Class 10,000 clean rooms, or ISO Class 7 clean rooms, have a higher particle concentration limit compared to Class 1,000 clean rooms. The maximum allowable particle concentration in a Class 10,000 clean room is 10,000 particles of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. Class 10,000 clean rooms find applications in industries such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, biotechnology research, and food processing.
Class 100,000: Standard Industrial Environments
Class 100,000 clean rooms, or ISO Class 8 clean rooms, have a higher particle concentration limit compared to Class 10,000 clean rooms. The maximum allowable particle concentration in a Class 100,000 clean room is 100,000 particles of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. These clean rooms are typically utilized in standard industrial environments where a lower level of cleanliness is required, such as general manufacturing and certain laboratory applications.
Conclusion
Clean room classifications provide a standardized framework for defining the level of cleanliness required in various industries. From the ultra-clean environments of Class 1 clean rooms to the controlled industrial environments of Class 100,000 clean rooms, each classification serves specific purposes and applications. Understanding clean room classifications is essential for ensuring compliance with cleanliness standards, maintaining product quality, and protecting sensitive processes in industries where contamination control is critical.
FAQ
Q1: What is a clean room?
A clean room is a controlled environment designed to minimize particulate and microbial contamination. It is used in industries where cleanliness is critical, such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics, healthcare, and aerospace.
Q2: How are clean rooms classified?
Clean rooms are classified based on the number and size of particles allowed per cubic meter of air. The classification system follows standards such as ISO 14644 which defines cleanliness classes ranging from ISO Class 1 (the strictest) to ISO Class 9 (the least strict).
Q3: What is the significance of clean room classifications?
Clean room classifications provide a standardized framework for defining the level of cleanliness required in different industries. They ensure that industries meet cleanliness standards, maintain product quality, and protect sensitive processes from contamination.
Q4: What are the particle concentration limits in different clean room classes?
Particle concentration limits vary for each clean room class. For example, in a Class 1 clean room, the maximum allowable particle concentration is 1 particle of size 0.1 micrometers or larger per cubic meter of air. The limits increase in higher clean room classes.
Q5: What industries use Class 1 clean rooms?
Class 1 clean rooms, with the strictest cleanliness requirements, are used in industries such as microelectronics, nanotechnology, and advanced optics, where even a minimal level of contamination can have a significant impact on the final product.
Kwang Cleanroom is proud to offer examples of a variety of our cleanroom projects below. Laminar Flow Clean Room, Clean Room Production, ISO Room, 100000 Level Purification Workshop, ISO 4 Cleanroom, Clean Room Level, Cleanroom ISO 6.
